North and South America were the last landmasses in the world to gain human inhabitance. The Native Americans did not arrive on the continent of North America by sailing there in ships from across the ocean. They walked to get to the Americas.
the first Native Americans arrived in Alaska
from Siberia less than 23,000 years ago
Although they took their time, over several thousand years, their ancestry is traced to both east Asian and western Eurasians that made their way from eastern Siberia into a new world at present-day Alaska around 40,000 years ago. The remains of an 11,500-year-old infant found by archaeologist reveal an Ice Age civilization in Fairbanks, Alaska
Asian and western Eurasians – Upward Sun River camp in Alaska
The Paleo people were hunger-gatherers that crossed into North America via Beringia, a land mass now under the ocean waters of the Bering Strait. Humans and animals could simply walk from Asia to North America.
Paleo Indian culture – Paleo Indians caribou hunting
The people living there would have had no idea that it was a land bridge at all. Native Americans likely arose from a single population of people who had lived in Beringia, isolated for many years.
Beringa land bridge
Beringia was also an ideal environment for large grazing mammals, giving early hunter-gathers something to hunt. Some of them probably followed the herds of bison, mammoth, and caribou across this land bridge, they were the first “big-game hunters.”
the hunter games
Melting ice made an open corridor, full of mud, ice and slush, allowing man and animals to travel a miserable journey south.
North American Indian migration
Others may have followed along the coast on shelf or sheet ice, and they may have traveled in small primitive boats along the northern Pacific.
primitive boats
The migration spread first along the coast then eastward. They were the first immigrants to the New World and they brought with them a culture that spawned into civilizations like the Iroquois in North America and the Piraha of South America.
Iroquois longhouse
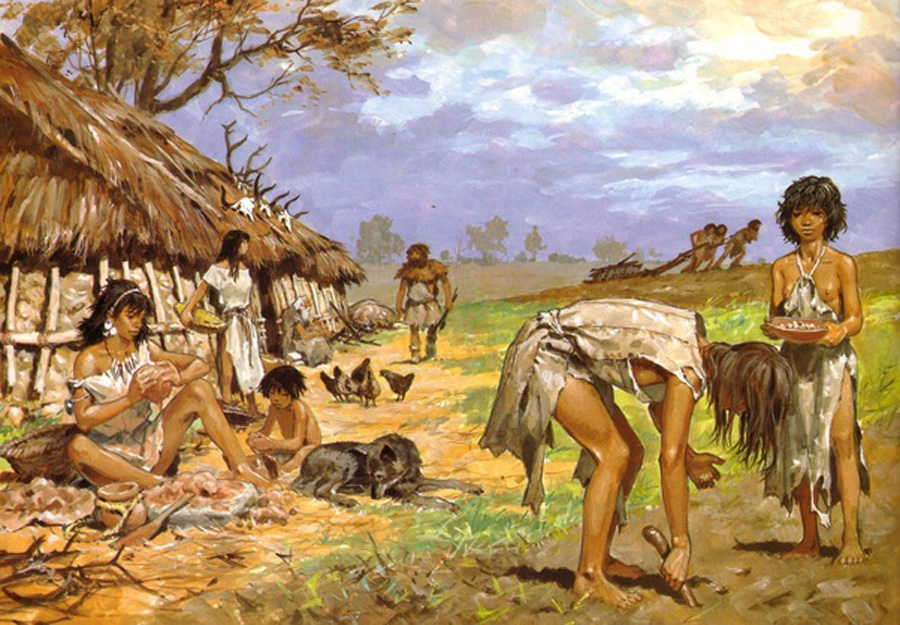
Over time, melting ice raised the sea level covering the land bridge and separating the human and animal population of the Old World with the New World. The Native Americans lost many of the immunities to diseases their ancestors had possessed. Several thousand years later the first complex civilizations arose as hunter-gathers settled into semi-agricultural communities.
hunter-gathers to farmers
Most Native Americans today are direct descendants of the Clovis people who settled across North America about 13,000 years ago. There is evidence of early human activity in the stone tools, spear and arrow heads, and scrapers that have been found by archaeologists. These hand- crafted lithic flaked tools are used to classify cultural periods. The earliest definitively-dated Paleo-Indians was the Clovis culture.
Clovis named for the first significant archaeological site found in 1929 near Clovis
Native Americans were isolated from peoples of the, “Old World” until about the 10th century when Norsemen explored and settled areas of North America.
Viking voyages to the new world
When Christopher Columbus landed in the New World he was in search of India and thought he had arrived in the East Indies. These islands were known as the “West Indies”, which let to the blanket term “Indies” and “Indians”, which implied racial or some kind of cultural unity among the indigenous peoples of the Americas.
the voyages of Christopher Columbus
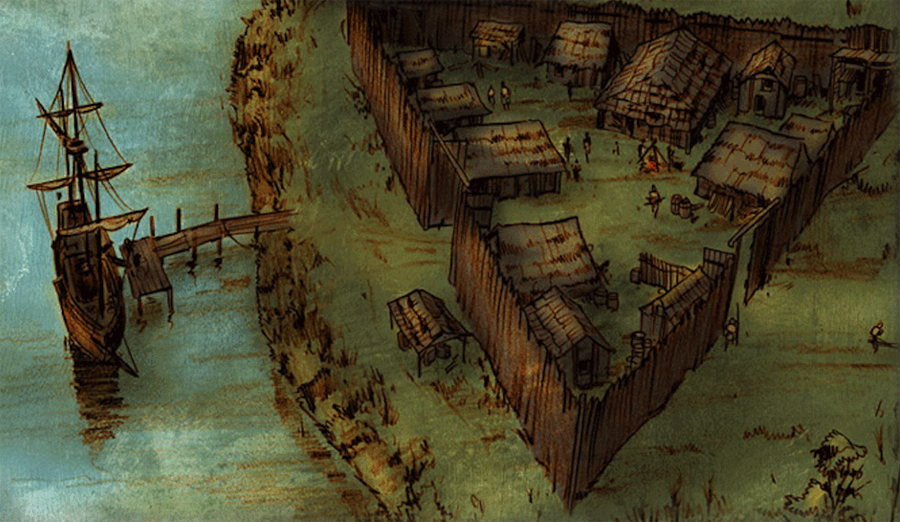
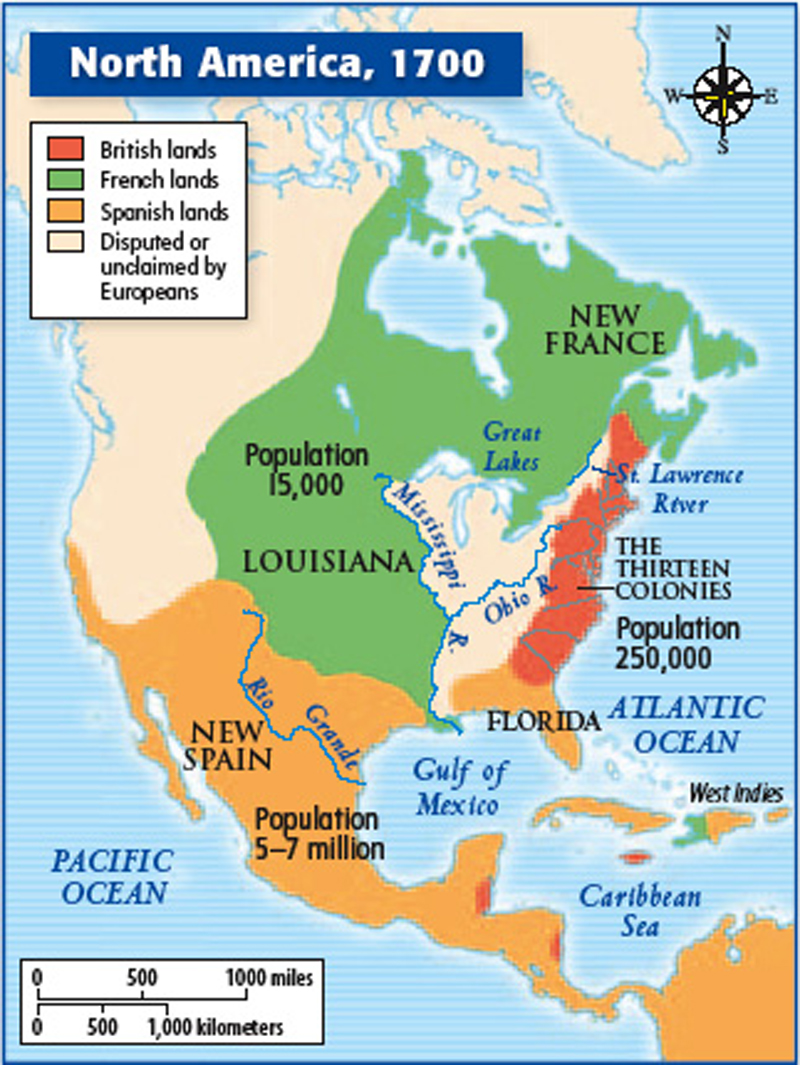
The European colonization of the Americas fundamentally changed the lives and cultures of the native peoples.
the colonization of the Americas – map of settlements
Within the first century of contact with the Europeans the Native American population diminished 80% and 90%. The Europeans brought diseases with them, like cow pox, they had acquired from their domesticated animals that the Native Americans did not have access to. Native American tribes were decimated from Afro-Eurasian diseases.
Native American decimated by Afro-Eurasian diseases
The Tainos of Hispaniola were the first indigenous group Columbus encountered, and within thirty years 70% of them had died. Afro-Eruasian disease outbreaks, like measles, smallpox and cholera ravaged their population because they had no immunity to the sickness. Early explorers and African slaves brought them from Europe. Central Africans slaves, who like the Native Americans lacked any resistances to the diseases of Europe and Northern Africa.
Bartholomew Columbus’s cruel destruction in Hispaniola
The tribes were punished for revolting against forced labor and religious education, this led to the last great Taino rebellion in 1511. Sadly, after years of mistreatment, the Taninos adopted suicidal behaviors. The men were jumping off cliffs to their death or eating untreated cassava, a violent poison. And some women were aborting or killing their infants to save them from a life of slavery.
Taino native peoples chose death over slavery
Soon after the voyages of Columbus, Spanish, Portuguese, and later English, French and Dutch sent colonial expeditions to the New World. They occupied and settled on the new discovered Indian homeland.
Discovery and settlement of the New World
Spain lay claim from the southwest, down through Florida and the Caribbean all the way to the southern most tip of South America.
Martin Afonso de Sousa founded the first permanent Portuguese settlement, Captaincy of Sao Vicente, in the Americas what was called “Port of the Slaves” in 1532. They trafficked in slaves captured by allied tribes.
Martin Afonso de Sousa – Early map of Brazil -São Vicente
English warships attempted to trade with the Portuguese settlement, but they were attacked by three Spanish galleons only to be repelled by the English ships sinking one Spanish galleon in the battle.
English repelled Spanish galleons
The English established colonies on the Atlantic and North Pacific coast of North America. English colony was founded on the success of commerical tobacco farming dating back to the 17th century when the first crop was planted. The industry originated in the production of tobacco for pipes and snuff. Economic opportunity was one of the main reasons people came to the New World.
France settled in Quebec and claimed other parts of central United States.
After some early trading expeditions, the Dutch first settlement in the Americas was founded in 1615 as Fort Nassau, on Castle Island on the Hudson. The settlement served mostly as an outpost for trading in fur with the native Lenape tribes people.
Fort Nassau & map – Lenape Indian – Fur trading
The Netherlands built a settlement, New Amsterdam now called New York. They also started colonies on some Caribbean islands and parts of northern South America.
Netherlands New Amsterdam ( New York)
Native Americans fought just as hard to keep their homeland as did the people that were trying to take it away from them. The European colonists massacred the indigenous tribes and enslaved them. And later, the North American Indian Wars of the19th century, killed 19,000 whites and over 30,000 Native Americans.
European colonists enslaved Native Americans
Late in the Archaic period about 4,000 years ago, Native American in the north began to shift from hunter gathers to farming communities that began the small-scale felling of trees. Archaic Indians began using fire in a controlled manner for clearing more land for farming. The deliberate burning of undergrowth was used like the effects of natural fires that tended to clear away forest and expose the bare soil. This made herbs and berry-producing plants that were important for food and medicine grow much quicker. The cleared land made traveling easier to get around. Pottery was becoming common and it became a way of dating archaeological finds.
Archaic Indians began farming and making pottery
When Europeans reached the Mississippi River valley they discovered the last major prehistoric cultural development in North America that was still in existence from 700 AD, where arranged burning had cleared land for agriculture which included nut and fruit trees.
Choctaw Indian encampment – Native American settlement on the Mississippi River
Domesticated wild crops by the Native Americans are still cultivated in modern times such as, squash, pumpkins, zucchini, acorn squash, butternut squash, the pinto bean, and maize or “corn” the most important crop in the world. Indigenous Americans produced, several verities of beans, tomatoes, potatoes avocados, peanuts, cocoa beans used to make chocolate, vanilla, strawberries, pineapples. The planted several verities of peppers, bell, Jalapenos, and paprika and chili peppers. Native Americans roosted sunflower seeds, made rubber, grew tobacco, and some types of cotton.
These three crops were grown together, with the pole beans using the stalk of the corn for support, and the squash protecting the soil from weeds.
The Menominee and Peuple Indian tribes of Michigan and Wisconsin held a longstanding “sacred values” about hunting and fishing. They only took what they needed at the time, always giving thanks and prayers to mother earth for the rivers bountiful catch.
Peuple tribe – Menominee tribe family winter home
Native American peoples that were isolated developed similar skills and a communal society even though some tribes never made contact with each other.
Native American survival skills
Native American Indians of the northern great plains shared the behaviors of roaming hunter-gathers that wandered after the great herds of buffalo. The nation’s buffalo almost became extinction by government encouraged mass killings.
Native American staple foods – buffalo roamed wild – cleaning the hide
North American Indians spoke 56 different languages, and gesture language was highly developed among them. Picture writing on rocks and walls of caves show a concentration between art and storytelling.
North American language – Petroglyphs – White Horse’s winter count
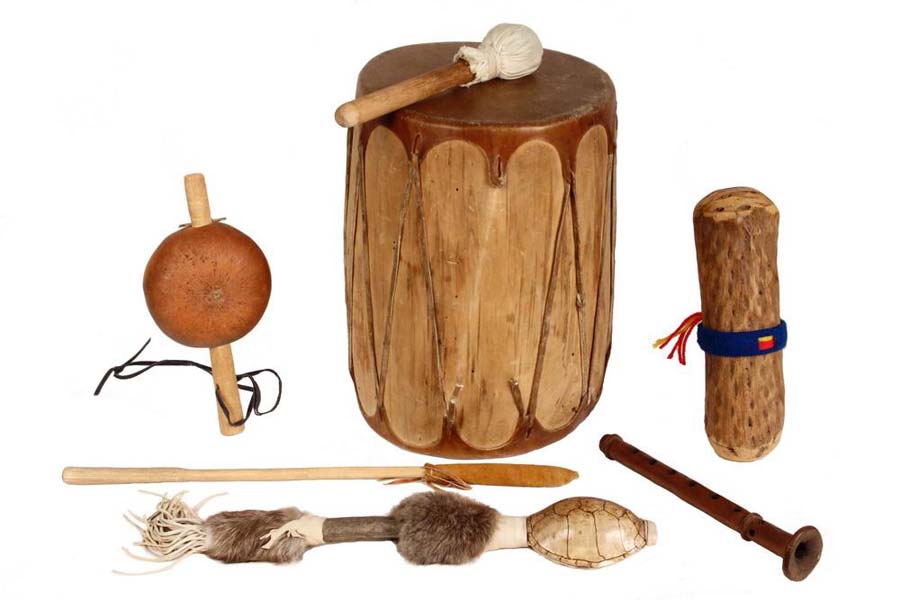
Music was a very important part of Native American culture. The rattles, clapper sticks, and rasps focused on the percussion of the drums, while flutes made of river cane or wood and string bowed instruments all joined in.
Native American musical instruments – flute player – Apache bowed string instrument
Making smoke, the sharing of tobacco, was used to build trust and trade among the tribes. Native Americans advanced in trade, spiritual and communal pecking order. After generations of Metis and Inuit married European colonists a culture was developed of small farmers, hunters and trappers. They were usually Catholic and spoke French.
Algonquin trade with Iroquoise – Metis culture – Inuit culture
The European Canadians encouraged Native Americans abandon their traditional practices and beliefs and conform to conventional European ideas of Canadian culture.
Native Americans in Canada
Indigenous peoples of the Americas were called “Indians” by Columbus when he though he had discovered the East Indies and this became the name of all native peoples. In the 20th century some of these peoples insisted on being identified as “Native Americans and this was approved by the U.S. Census Bureau and additional parts of the government.
Columbus and the Indians – Native American
>>to return to previous page – right click on back arrow <<